
We constantly hear about plant medicine clinics churning through patients and handing out scripts without providing adequate patient care.
Changing clinics can be costly. The team at Ananda is taking a stand against substandard care by making it affordable to switch.
We’re now offering a clinic transfer consult for $99 – in clinic or telehealth for those with a discharge letter.
To book a clinic transfer appointment you can call the clinic on (02) 5624 5024 or book online.
For online bookings:
– Click on the Book Now button above
– Select clinic or Telehealth
– Choose doctor and select ‘New Patient’
– Here you will have the option to select ‘Clinic Transfer’
Unsure if this applies to you? Call the clinic and ask to speak with one of our nurses if you have any questions before booking – nurse chats are free.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
As many of you are aware Ananda Clinics works with a small, hand picked group of medicine producers to offer our patients only the highest quality, Australian grown medicines from ethical suppliers. Another important criteria we require is that the companies we work with participate in university level research that will help the industry grow, address the stigma, and ultimately increase access to medical cannabis for those it may help.
One of the companies on our preferred list is currently involved with a research study, to investigate the quality of life, health and economic impact of medicinal cannabis on patients with chronic disease.
At Ananda Clinics, we aim to increase the well-being of our patients and our community by staying up-to-date with critical studies, emerging research and breakthrough information. We’re always excited to see new research in the field such as the Global QUEST initiative.
The QUality of life Evaluation STudy (Global QUEST Initiative), conducted by researchers at Curtin University, aims to be the world’s largest longitudinal clinical study investigating the quality of life, health and economic impact of medicinal cannabis on patients with chronic disease.
Patients accessing medicinal cannabis generally have a range of conditions and symptoms that impact their quality of life. This clinical study sets out to better understand and measure how these conditions and symptoms affect patients’ quality of life over time, as well as any ‘out of pocket’ costs, while they are accessing medicinal cannabis as a treatment option.
The results from this study will help future patients to understand the potential impact of medicinal cannabis on their overall quality of life.
You may be eligible to participate if you:
To make an appointment call Ananda Clinics reception on 02 5624 5024
Find out more information about the Global QUEST initiative at thequestinitiative.com
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
Inflammation is the body’s natural immune response to protect itself from injury, infection or harmful stimuli. When the body detects a threat, the immune system initiates an inflammatory response. Inflammation is crucial for eliminating potentially harmful agents and promoting healing, however, excessive or ongoing inflammation can result in significant damage. In fact, inflammation plays a central role in the development of many diseases and chronic conditions.
There are many diseases known for chronic inflammation such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis. However, according to the Centenary UTS Centre for Inflammation, inflammation is increasingly being found to play crucial roles in the development of many major diseases, including Alzheimer’s, heart disease, cancer, respiratory diseases, diabetes, tuberculosis and COVID-19.

The Endocannabinoid System plays a crucial role in modulating inflammation and maintaining immune homeostasis. When inflammation occurs, endocannabinoids are produced and bind to cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB2 receptors, on immune cells. This interaction can have anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing the release of pro-inflammatory molecules and reducing immune cell activation.
The ECS can also indirectly influence inflammation by interacting with other systems in the body. For example, endocannabinoids can affect the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which can modulate pain perception and mood, ultimately impacting the inflammatory response.
Cannabinoids such as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), can also interact with cannabinoid receptors and modulate inflammation. However, the use of cannabinoids for inflammation is an area of ongoing research, and more studies are needed to fully understand their therapeutic potential and optimal usage.
Further understanding the functioning of the ECS may provide insights into developing new therapeutic approaches for inflammatory conditions and related diseases.
Find out more by Booking an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
At Ananda Clinics a fundamental part of our practice is treating the signs and symptoms of imbalances in the body. Some of those imbalances show up as a chronic illness, chronic stress, insomnia, or hormonal imbalances.
All of the symptoms that we see are impacted by the dysregulation of our body’s natural sense of equilibrium, called homeostasis.
All living creatures, animals, plants and people need their bodies and systems to function optimally in order to live a long and healthy life. This process of optimal function is called homeostasis, or physiological equilibrium.
Homeostasis ultimately refers to the self-regulating process of the body that constantly seeks and maintains a stable internal environment despite external changes and stressors. It is a critical, whole body process that ensures that vital functions (like temperature) are maintained within a narrow, optimal range. Homeostasis involves several physiological systems, including the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems, which work together to maintain homeostasis.
Essentially, your body maintains different baselines for a healthy body (temperature, stress, sleep). When the baseline becomes under or over its optimal range, homeostasis will work to correct it, for example, in order to re-regulate body temperature when you’re too hot, you sweat, and when you get too cold, you shiver.
Homeostasis ultimately works by manipulating different ions and molecules in the body to maintain balance through a physiological reaction that switches on until balance is reached and impacts things like:
Homeostasis is essential for survival and is a coordinated effort by the body’s internal systems to do exactly that – survive.
The body must maintain stable internal conditions to carry out essential, everyday functions like circulation, respiration, digestion, sleep, and changes in stress. Any imbalance in the body can lead to dysregulation, which can have severe, long term consequences if not managed effectively.

Any imbalance or dysregulation in the body and Endocannabinoid System, chronic or acute, can lead to the disruption of the body’s homeostasis. When homeostasis is disrupted, symptoms of that dysregulation can quickly start to show and impact your life – think pain, insomnia, and anxiety.
An example of homeostasis and dysregulation at work is the oh-so-common stress response; when the body is exposed to stress, the adrenal glands release the stress hormone cortisol to help the body manage stress in the moment, before returning to rest. This in-the-moment response is intended to help your body and brain react to stress or danger and to react quickly.
However, prolonged exposure to stress can lead to the chronic cycle and elevation of cortisol, which can have long term negative effects, like increased weakened immunity, sleep disturbances, and weight gain.
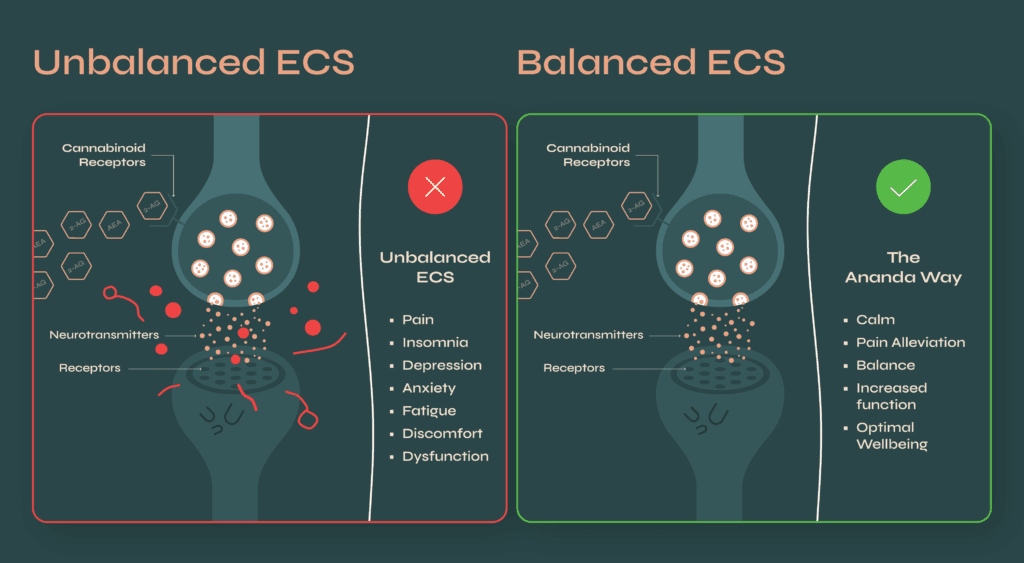
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is considered our ‘Master Regulator’ and plays a vital role orchestrating balance and function in the brain, endocrine and immune systems in all humans. Our ECS influences many critical functions in the body, including: sleep, pain, inflammation, immune responses and emotional processing. Essentially, it enables optimal human performance.
The ECS is made up of a network of chemical signals and cellular receptors, CB1 and CB2, that are regulated by naturally produced molecules called endocannabinoids, which are produced by the body, and can be replicated with plant-based medicine.
For example, activating CB1 receptors found in the brain, leads to the release of dopamine, which can help balance mood when you are feeling dysregulated. The ECS plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body, by activating its own receptor sites to help regulate various physiological processes, like:
Maintaining and regulating homeostasis in the body should be a priority for long term health and wellness and can help to relieve symptoms associated with stress, anxiety, sleep disruptions, and more.
There are several simple, effective ways to maintain and support homeostasis in the body:
Find out more by Booking an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
We learn all about the body, its functions, and how to manage its overall wellness at an alarming rate every-single-day.
We know about heart health, circulation, digestion, the importance of muscle growth, and nervous system regulation as a part of staying healthy – but there is one glaring gap in this story. One critically important system that is constantly overlooked and under-researched …
And that is the body’s own Endocannabinoid System (ECS).
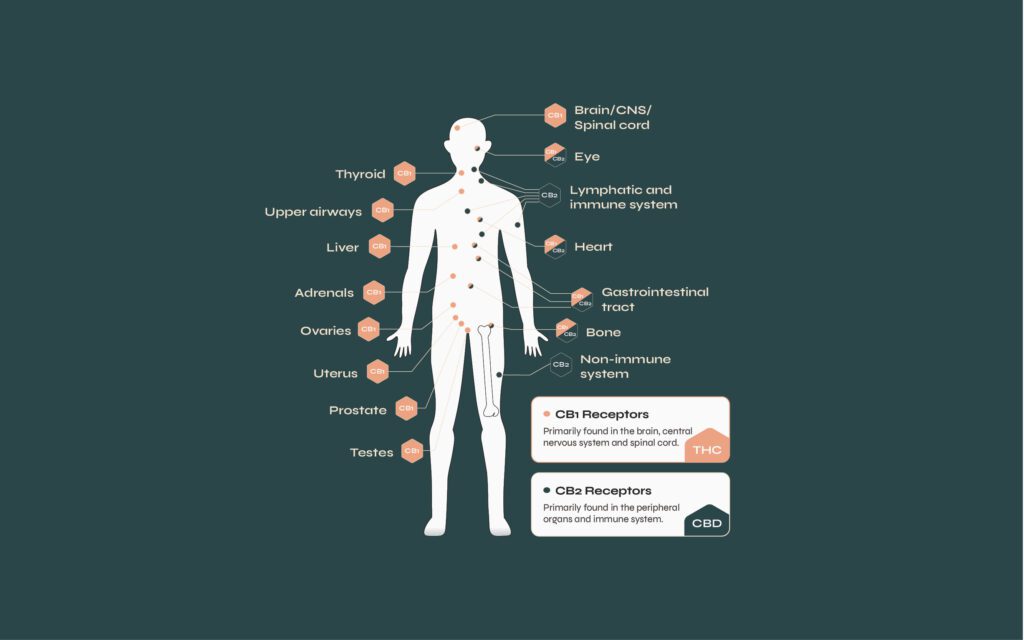
The endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a critical modulatory system, considered our ‘Master Regulator’, and plays a vital role orchestrating balance and function in the brain, endocrine and immune systems in all humans (and animals too).
It has been described as being perhaps the most important physiological system in establishing and maintaining health and this is done through maintaining homeostasis, or balance.
Our ECS influences many critical functions in the body, including: sleep, pain, inflammation, immune responses and emotional processing. Essentially, it enables optimal human performance through a network of chemical signals and receptors that are regulated by naturally produced molecules, called endocannabinoids.
Similar to other regulatory body systems, the ECS influences at least 15 major functions in the body:
It is also the key system activated by therapeutic cannabinoid medicine through the interaction of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors naturally existing in the human body.
To understand how the the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) works, you should first know that it is made up of two distinct parts:
Cannabinoids are the name given to all chemical substances that help communicate and join cannabinoid receptors and the brain. Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring molecules produced by the body ‘as needed’ to help maintain homeostasis, or internal balance, in the body. Endocannainoids are also called endogenous cannabinoids, and produce two key kinds:
These key endocannabinoids are produced, released, and interact with endocannabinoid receptors to keep your body and nearly all of its functions operating optimally.

Endocannabinoid receptors receive and interact with endocannabinoid molecules are have, again, two key placements in the body:
CB1 receptors are primarily located throughout the Central Nervous System (CNS), and in particular the brain, also making these receptors part of the psychotropic effect of some medicinal components. These receptors, once activated by endocannabinoid molecules, help to enhance or moderate the release of neurotransmitters, influencing things like pain.
CB2 receptors are primarily found in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and throughout the immune system, playing a huge role in reducing immune responses, like chronic and acute inflammation.
As a naturally existing biological system, the ECS regulates the release of endocannabinoids and the interaction with endocannabinoid receptors to help maintain homeostasis within your body.
The ECS is triggered by day-to-day activities like vigorous exercise, inflammation, pain, temperature changes and much, much more. Once activated, the endocannabinoid system sends out its endocannabinoids, or chemical messengers, to the different receptors sites as needed. Each endocannabinoid produced and released then binds to one of many receptors found all over the body (CB1+ CB2), effectively activating your body’s own ability to rebound, recover and heal.
When a receptor is engaged, whether it be a CB1 or CB2, things like pain, inflammation, anxiety, insomnia and seizures are regulated.
Dysfunction of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) can lead to unpredictable symptoms like, anxiety, depression, inflammation, insomnia, and uncontrollable mood swings.
Phytocannabinoids (phyto- meaning ‘from plants’), are naturally occurring molecules found in numerous plant species. Phytocannabinoids have a nearly identical chemical structure to the endocannabinoids naturally produced by the body and interact with receptor sites in nearly identical ways.
When ingested in precise, measured ways, phytocannabinoids can replicate our body’s natural endocannabinoids in order to regulate and influence the bodys’ neurological, endocrine, immune, and nervous system responses.
Ready to find out how your Endocannabinoid System may be influencing your symptoms, and can be used to help relieve those symptoms?
Find out more by Booking an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
All plants get their aroma, colour, and flavour from naturally existing compounds that are found in all species of plants (and even some animals).
These compounds, called terpenes or terpenoids, play a central role in medicinal properties, therapeutic benefits, and individual effects of plant-based medicines, and play an important role in the impact of plant-medicine on the body’s Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
They are also one of the most abundant compounds in the world.
Terpenes have been used and applied for thousands of years in herbal medicine. All plants contain and synthesise several hundred terpenoid compounds as a part of their chemical makeup, and medicinal properties..
These terpene compounds are considered the essential oils of plant life and are regarded as a cofactor in overall therapeutic benefits. Terpenes are a type of organic compound and are also responsible for giving plants their distinct aroma and flavour, and can even be found in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices.

Terpenes have two distinct counterparts:
As a compound, terpenes can have a wide and varied influence on the effects of plant-medicine and plant-based therapies and work synergistically with both cannabinoids and flavonoids; plant compounds with a variety of health benefits. This is known as the Entourage Effect, where each compound influences the effect of the other – in harmony.
According to research, terpenes have the ability to work with the endocannabinoid system to augment therapeutic effects, suggesting that cannabinoids and terpenes work together to change the body’s endocannabinoid tone through the body’s own Endocannabinoid System (ECS). Different terpene profiles can influence the effects and impacts of cannabinoids, ultimately creating individual responses to varying compounds.
Terpenes can influence the ECS in different ways, but can have energising, uplifting effects, or calming, relaxing effects (to name a few). In addition to their effects on mood and energy levels, terpenes show other potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory properties, while others have been shown to have analgesic (pain-relieving) effects.
At Ananda Clinics, we rely on The Ananada Way (link to Our Approach Page) to establish the precise ratios of cannabinoids and terpenes to regulate and influence the body’s Endocannabinoid System in specific ways. By tailoring each prescription for each patient, plant-based medicine can be apply in very specific ways to produce very specific outcomes.

In nature terpenes might be present in a citrus plant, acting as a natural citrus repellent to bugs, in lavender as a calming aroma, and in pine needles, lending the signature pine scent.
Just like in nature, terpenes found in plant-based medicine can have unique physiological benefits and can impact a variety of symptoms.
Myrcene (mur-seen): The most widely cultivated and abundantly dominant terpene
Limonene (LIM-o-neen): can modulate certain immune cell behaviours and is safe for therapeutic supplementation
Caryophyllene (carry-OFF-uh-leen): only terpene that interacts with the body as an cannabinoid
Pinene (PIE-neen): most abundant in nature
Linalool (LINN-uh-lool): the most important company in aromatherapy for its calming and anti-anxiety effects
Ocimene (Oh-sih-mene): most commonly used in perfumes and fragrance
How could terpenes be used to create a healthier Endocannabinoid System and alleviate your symptoms?
Find out more by Booking an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
Women have held a long-standing relationship with medicinal herbs, wisdom, and rituals throughout history.
Going as far back as ancient Egypt, women have been utilising plant-based medicine for pain and stress relief. Dating back to at least 1500 BCE ancient Egyptian texts describe endocannabinoid medicine to help manage and control labour pain.
In the 1800’s the British Medical Journal, published two research papers about the application of medicinal cannabis for menstruation and bleeding.
And in 1988, scientists were able to tie the story together after discovering the body’s own regulatory system, the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), at which point the connection between the female reproductive system and cannabis as medicine really clicked.
As a critical modulatory system, the Endocannabinoid System is known as our body’s ‘Master Regulator’, influencing at least 15 major functions in the human body, including:
The (ECS) is a complex network of neurotransmitters, receptors, and enzymes that play a vital role in regulating various physiological processes in the body, including reproductive health. The Endocannabinoid System (link to blog: What is the ECS?) has two key receptor sites that are located throughout the body, called CB1 and CB2 receptors.
It has been described as being perhaps the most important physiological system and enables optimal health through a network of chemical signals and receptors that are regulated by naturally produced molecules, called endocannabinoids.

The ECS is an essential regulator of women’s reproductive health, with its receptors found in key reproductive organs and tissues, and are particularly concentrated in the ovaries. It’s shown to play a crucial role in the regulation of the female reproductive system, including the:
The ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes are highly concentrated in CB1 receptors, with CB2 receptors existing predominantly in the immune cells of the reproductive system. Research shows that the ECS also plays a critical role in hormonal regulation, with CB1 activation potentially impacting oestrogen and progesterone levels, which are essential for regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting pregnancy.
The Endocannabinoid System is closely associated with the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian Axis (HPO) creating a two-way communication network between the ECS, the HPA and steroid hormone production and effective secretion.
The ovaries and other hormone regulating systems (like the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland) are also shown to have both CB1 and CB2 receptors and influenced by the dysregulation or regulation of the body’s endocannabinoid system.
The imbalance and dysfunction of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) has been linked to a number of female reproductive disorders, particularly endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Dysfunction of the ECS system can also act as a contributing factor in a number of co-existing symptoms and imbalances in the body including pain, anxiety, depression, fatigue, insomnia, and temperature regulation.
Treating the Endocannabinoid System can help to manage and treat those symptoms associated with reproductive changes and disorders:
Regulating the ECS takes a multi-functional approach to relieving symptoms of menopause, like: irritability and mood changes, dysregulated metabolism, stress, nervous system dysfunction, and chronic pain.
As a chronic condition, people with endometriosis can suffer from a variety of symptoms, including that can present as dull, to unbearable. Balancing the ECS can help to bring relief to symptoms like: pain, heavy periods, bloating, anxiety, and fatigue.
Treating the ECS can help to treat and manage symptoms of PCOS, including: hormone secretion, pain, and infertility.
Chronic pain typically is most commonly associated with PCOS, endometriosis, and inflammation. Treating dysfunction of the endocannabinoid system can help to regulate and control pain, in addition to its associated symptoms: insomnia, irritability, anxiety, and depression.
As a closely related regulatory body system, the ECS has an influence over nervous system regulation, playing a key role in the symptoms of nervous system dysregulation, including anxiety and depression. A common side effect of reproductive disorders and hormone imbalances, the ECS can help manage these symptoms.
Working directly with the Endocannabinoid System to create homeostasis, Ananda Clinics prescribes precise compounds to help treat reproductive health, or dysfunction at its core. Find out more by Booking an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
Stress is a completely natural human response that we, for the most part, completely ignore, overlook, and misunderstand on a day-to-day basis.
It can strike at any place, any time, and anywhere without warning from a variety of sources, like: work, family, home, relationship, health, or financial worries. Some stress is bad, and in fact, some stress is actually good.
Stress can come from many sources, including work, relationships, finances, and health concerns. While some stress is normal and even healthy, chronic stress can lead to a range of health problems. It can prevent you from sleeping, living, and enjoying life if you have too much, and prevent you from growing if you don’t have enough.
Feeling ‘stressed out’ comes with a multitude of symptoms, but looks a little different for everyone.
Stress functions throughout a constellation of physiological systems in the body by evoking rapid shifts and changes in neuro behavioural processes. Stress is the body’s natural response to triggers, called the ‘fight-or-flight response’, and functions as an evolutionary warning sign that we are in ‘danger’.
When you experience stress it triggers your fight-or-flight response, flooding the body with stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline to help you manage and adapt to the stress. Although it’s a normal response, stress can become a problem when those responses stay triggered for long periods of time, or you remain chronically stressed out. Stress creates an allostatic load in the body. This is due to disrupted allostasis which is the word given to the active process of maintaining homeostasis. We are beginning to understand that multiple diseases in the human body are due to the creation of this allostatic load.
Both physical stress: high impact workouts, manual labour, physical danger and mental stress: financial, family, health worries, can both have distinct impacts on your day-to-day and long term health, making stress management critical to your health.
When you’re under stress, your body produces more cortisol more regularly, which keeps you awake. Cortisol can disrupt your sleep by making it hard to fall asleep, stay asleep, or sleep at all. Without sleep your body doesn’t heal, repair, and regenerate and can severely impact your mood. Lack of sleep ultimately leads to more stress, creating a vicious cycle of sleep deprivation.
Stress can also impact your nervous system, which is responsible for controlling your body’s response to stress in the first place. With the triggering of your body’s fight or flight response and the release of stress hormones, your nervous system responds accordingly with a heightened, uncontrollable sense of awareness.
Although this response can be life saving in the right circumstances, and in short bursts, chronic stress can lead to a constant state of hyperarousal in the nervous system, which can manifest in physical symptoms like muscle tension, headaches, and digestive problems.
The Endocannabinoid System plays a key role in regulating a range of bodily functions, including mood, appetite, and pain. When you’re under stress, your body’s endocannabinoid system can become dysregulated, leading to a range of symptoms and health problems.

The body’s own Endocannabinoid System is known as the body’s master regulator and helps to control things like stress, anxiety, mood, sleep, and healthy nervous system function. This system works by producing its own natural compounds, called endocannabinoids, to activate the ECS when needed. The precise balance of these compounds keeps the body in a state of homeostasis, or balance.
One of the key ways that stress impacts the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is by reducing the production of endocannabinoids, causing dysregulation of the body and contributing to feelings of anxiety, depression, and chronic stress. Chronic stress can lead to the downregulation (a decrease in the number of receptors on the surface of target cells) of cannabinoid receptors, which can make it harder for your body to respond to endocannabinoids and other compounds that activate the system.
The human body naturally produces endocannabinoids, the most abundant being anandamide and 2-AG. A growing body of work indicates the ECS is an internal regulator of this stress response, with some studies showing that stress evokes bidirectional changes in critical endocannabinoids, anandamide (AEA) and 2AG. Where stress reduces anandamide* levels it equally increases 2AG**. A reduction in anandamide (the bliss molecule), appears to contribute to the stress response, activation of the Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis (increasing anxiety), and rising 2AG levels including changes in pain perception, memory and synaptic plasticity.
*Anandamide (AEA) – an endocannabinoid, often referred to as the bliss molecule
**2-AG – an endocannabinoid, a signalling lipid in the central nervous system, and key regulator of neurotransmitter release
Regulation and healthy function of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) buffers against the effects of stress to help maintain an effective state of physical and emotional homeostasis.

Creating a simple, consistent stress management routine can be incredibly impactful and necessary for long term health and wellness. Current research is highlighting how all of the above improve our wellbeing through the support and stimulation of the endocannabinoid system.
Here are Ananda Clinics top recommendations for a simple, easy to implement stress-management routine:
1. Sleep: Making sleep a priority can help to reduce the impact of stress on your body. Try to establish a regular sleep schedule and create a calming bedtime routine to help you relax and unwind: put phones away, cut blue light exposure, dim the lights.
2. Exercise: Regular exercise can help to reduce stress and boost your mood. Even a short walk or gentle yoga practice can be helpful. Stress, walk, and use gentle practices for movement at least 3x per week.
3. Mindfulness: Mindfulness practices (link to blog: Mindfulness Practices for your health) like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help to reduce stress and calm your nervous system. Implement 60 seconds of box breathing in the morning and at night to reset your nervous system.
4. Community: Connecting with a community can help to reduce feelings of isolation and stress. Try to make time for meaningful social connections, whether it’s spending time with family and friends or finding a community from activities you enjoy.
5. Regulate your ECS: The endocannabinoid system can quickly become dysregulated through exposure to stress. Through a healthy diet rich in omega 3 and 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, weekly exercises and meditation, and a healthy, connected social network help to regulate endocannabinoid levels and ECS function. Regular mindfulness and meditative activities have also been shown to modulate endocannabinoid levels, with anandamide being the primary molecule produced to exert positive, mood lifting effects through.
Find out more about how stress could be impacting your health, and how regulation of your Endocannabinoid System could help! Book an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
The human body is a complex machine that requires constant regulation. The body’s regulatory systems work in real-time to respond to external triggers like stress, temperature changes, pain, and hormonal changes, helping your body to find optimal health, wellness, and balance long-term.
We have a total of 11 major organ systems and a handful of key regulatory systems (and rhythms) that work synergistically to keep our bodies happy, healthy, and regulated each and every day.
Understanding how these systems work, how to keep them in balance, and how to recognise signs of imbalance is the first step forward in long-term health.
Didn’t know you had one?
You’re not alone.
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a complex system of receptors and chemical messengers that help regulate various functions in the body, including sleep, appetite, mood, and pain sensation. Only discovered in 1988 the ECS is now referred to as one of the most important physiological systems and is known as your body’s ‘Master Regulator’.
The ECS works by producing endocannabinoids, which are naturally occurring compounds that bind to cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems. This binding helps regulate the communication between nerve cells and modulate the release of neurotransmitters, promoting a state of balance and homeostasis.
A dysregulated ECS can result in various health problems, including mood disorders, sleep disturbances, anxiety, depression, and chronic pain. Symptoms of a dysregulated ECS may include changes in mood or appetite, sleep disturbances, and increased sensitivity to pain. If you suspect that your ECS is dysregulated, it’s important to seek professional medical advice and work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
The nervous system is made up of two parts, the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), with both playing a critical role in regulating and controlling balance, pain, inflammation, and stress in the body.
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and the PNS includes all of the nerves outside of the CNS. These two parts work synergistically to signal pain, inflammation, or dysregulation in the body to the brain, and to then carry chemical signals to these parts to regulate and rebalance the dysregulation in real-time.
The nervous system also helps to regulate stress, inflammation, and pain by releasing neurotransmitters that communicate with other parts of the body. The nervous system can also stimulate the release of hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which help regulate the body’s stress response.The nervous system can also help regulate inflammation by modulating the immune response, and it can help regulate pain by transmitting and modulating pain signals.
The body’s endocrine system helps regulate various physiological functions by producing and secreting hormones that influence things like growth and development, metabolism, and sexual function. Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream and bind to specific receptors on target cells, to create reactions in the body.
The endocrine system also consists of several glands, including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pancreas, which produce hormones that regulate sleep and wake cycles, stress, energy, and hormonal cycles.
A dysregulated endocrine system can lead to various health problems, including hormonal imbalances and disorders such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, diabetes, and infertility. Red flags associated with a dysregulated endocrine system may include chronic fatigue, changes in weight (gain or loss), skin and hair, mood, and sexual function.
The body’s sensory system is responsible for receiving and processing sensory information from the environment and transmitting it to the brain for interpretation. The sensory system includes various specialised receptors in the skin, eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and joints that detect changes in light, sound, temperature, pressure, and other stimuli. This information is then transmitted to the brain through the peripheral nervous system (PNS), where it is interpreted and used to regulate various functions in the body.
A dysregulated sensory system can result in sensory processing disorders including oversensitivity or under sensitivity to stimuli, difficulties with motor coordination, and difficulties with attention and focus. Over or under stimulation can play a role in sleep disorders, mood swings, anxiety, depression, and more.

Circadian Rhythm, also known as the body’s internal biological clock, regulates various functions in the body, including sleep, hormone secretion, and metabolism. Circadian rhythm is controlled by a group of neurons in the brain that are sensitive to light and dark, which sends signals throughout the body that it’s time to get energised, or to decompress and rest. This internal clock helps to coordinate the body’s functions with the 24-hour cycle of the day, promoting a state of balance and homeostasis.
A dysregulated circadian rhythm can quickly lead to sleep disorders, insomnia, mood disorders, hormonal imbalances, and sluggish metabolism. It is also the cause of ‘jet lag’. Symptoms of a dysregulated circadian system can include difficulty falling asleep or staying awake, grogginess or fatigue during the day, and changes in appetite or metabolism.
Balancing this system involves establishing a consistent sleep schedule and intentional exposure to natural light during the day, as well as avoiding exposure to bright lights and screens in the evenings – we recommend blue light blocking glasses at least two hours before bed.
Ananda Clinics specialises in the regulation of the Endocannabinoid System, which can help impact dysregulation in other systems, like the nervous, endocrine, and circadian systems.
To find out more about how your Endocannabinoid System can help to reset and regulate your symptoms, book with one of our GP’s today.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
It’s no surprise that in an increasingly on-demand world, we need to take increasingly good care of our health – and in an age of information, it feels like we need to do all the things, all at once to stay ahead.
And it’s a lot.
While a wide range of diet, lifestyle, and genetics play a role in our health, there will always be different things that work for different people. But for the majority of people there are a few key fundamentals that will prove to have a significant impact on long-term health, wellness, and overall vitality.
So if you, like so many of us, are looking to make a few small lifestyle changes that can have a big impact, follow along.
Sleep is one of the most important biological functions and is essential for life. Some studies even show that after being awake for 17 hours you could be considered legally intoxicated (comparable to a BAC 0.05%).
Good sleep hygiene is critical for overall health and for allowing the body to repair and rejuvenate, detoxify, rid the body of cellular waste, fight oxidative stress, and fight ageing. Research has shown that people who get adequate sleep are more productive, have better memory and concentration, and have a lower risk of developing chronic health problems such as heart disease, obesity, and depression.
Creating a consistent bedtime routine, avoiding stimulants, creating a sleep-conducive environment, and limiting screen time can help create a consistent sleep schedule which will help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle long-term.

Our bodies are made up of 60% water, helping to regulate and optimise physiological functions such as regulating body temperature, flushing out toxins, and transporting nutrients. Proper hydration is also vital for brain function and for preventing dehydration, which can affect cognitive abilities.
Adequate water intake also helps maintain blood volume and improve circulation, reduce the risk of heart disease, and support the overall cardiovascular system. Water and fluidity helps to remove waste products, and keep joints lubricated, promoting energy and vitality.
Studies show that not only drinking water, but being near water regularly is good for your long-term health. What is now called Blue Mind Science studies the neurological responses that humans experience when in, near, or around water, and the positive impact it has on health.
Physical activity and movement are crucial for long-term health and for the optimal function of critical physiological and regulatory systems, like the Endocannabinoid System. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, improves cardiovascular and muscular fitness, increases flexibility and balance, and strengthens bones.
Moving the body also releases endorphins, natural mood boosters that can improve mental health and reduce the risk of depression and anxiety. Physical activity also promotes better sleep, reduces stress, and improves overall energy levels. Inactivity, on the other hand, can increase the risk of chronic health conditions and accelerate physical and cognitive decline.
Aim to incorporate at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity into your daily routine, a few times a week (150 minutes total per week). Getting a little extra movement in can be as simple as walking instead of driving, taking the stairs, or walking during lunch instead of sitting.

Known as the “sunshine vitamin” as it is primarily synthesised in the body through exposure to sunlight, Vitamin D is an essential hormone for the proper functioning of the immune system, the maintenance of strong bones, and may also reduce the risk of certain cancers, heart disease, and depression.
Sunlight exposure also regulates the circadian rhythm, promoting better sleep, and boosting overall mood. Deficiency in vitamin D can lead to weak bones, increased risk of infections and chronic diseases. Getting enough sunlight and vitamin D is important for overall health and well-being, so it’s recommended to spend at least 15 minutes a day getting direct, unfiltered sunlight exposure into your eyes and on your skin (without looking directly into the sun). Be sure to wear protective clothing and a hat when the sun is at its strongest.
Human beings are social creatures and social connection through friends, family, and community has been shown to promote better mental health, reduce stress, and increase life satisfaction.
Being part of a community provides a sense of belonging and purpose, helps build resilience and reduces the risk of depression and anxiety. Physical affection like hugs, handshakes, and touch also play a role in promoting physical and mental well-being. Touch releases oxytocin, the “feel-good” hormone, which reduces stress and promotes feelings of safety and security.
Not only does this connection increase the ‘feel-goods’ but also reduces the ‘feel bads’ like stress, isolation, and feelings of depression. Connection is vital to feeling a sense of belonging and emotional support throughout your life, so seeking opportunities to feel connection, affection, joy and community are a key foundation for long-term vitality and wellness.
These key steps act as a great foundation for long-term health, but it will always be a work in progress.
Find out more about how you can naturally keep your body, nervous system, and Endocannabinoid System in an optimal state of healing and health by speaking with one of our GPs today.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
