
We learn all about the body, its functions, and how to manage its overall wellness at an alarming rate every-single-day.
We know about heart health, circulation, digestion, the importance of muscle growth, and nervous system regulation as a part of staying healthy – but there is one glaring gap in this story. One critically important system that is constantly overlooked and under-researched …
And that is the body’s own Endocannabinoid System (ECS).
The endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a critical modulatory system, considered our ‘Master Regulator’, and plays a vital role orchestrating balance and function in the brain, endocrine and immune systems in all humans (and animals too).
It has been described as being perhaps the most important physiological system in establishing and maintaining health and this is done through maintaining homeostasis, or balance.
Our ECS influences many critical functions in the body, including: sleep, pain, inflammation, immune responses and emotional processing. Essentially, it enables optimal human performance through a network of chemical signals and receptors that are regulated by naturally produced molecules, called endocannabinoids.
Similar to other regulatory body systems, the ECS influences at least 15 major functions in the body:
It is also the key system activated by therapeutic cannabinoid medicine through the interaction of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors naturally existing in the human body.
To understand how the the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) works, you should first know that it is made up of two distinct parts:
Cannabinoids are the name given to all chemical substances that help communicate and join cannabinoid receptors and the brain. Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring molecules produced by the body ‘as needed’ to help maintain homeostasis, or internal balance, in the body. Endocannainoids are also called endogenous cannabinoids, and produce two key kinds:
These key endocannabinoids are produced, released, and interact with endocannabinoid receptors to keep your body and nearly all of its functions operating optimally.
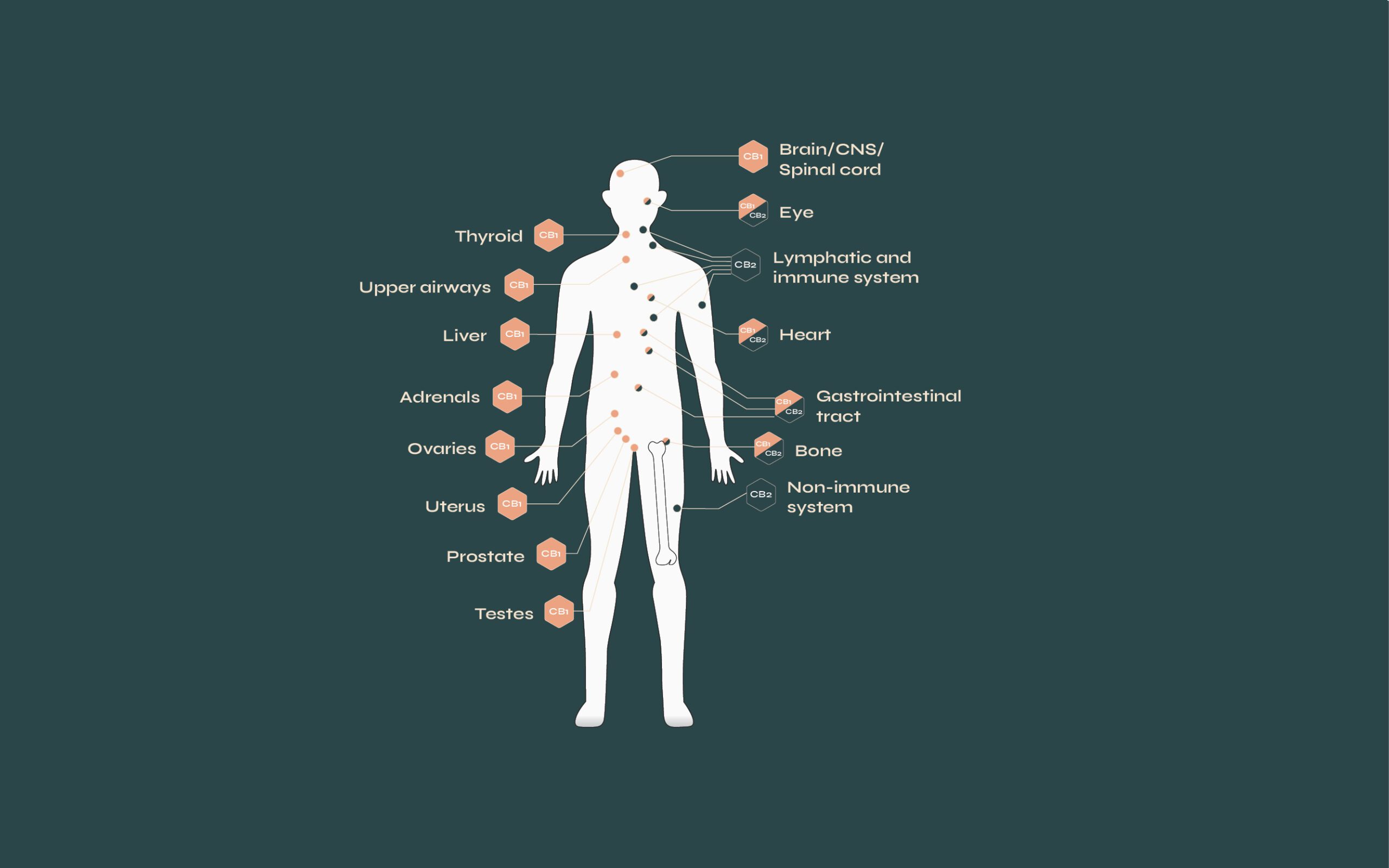
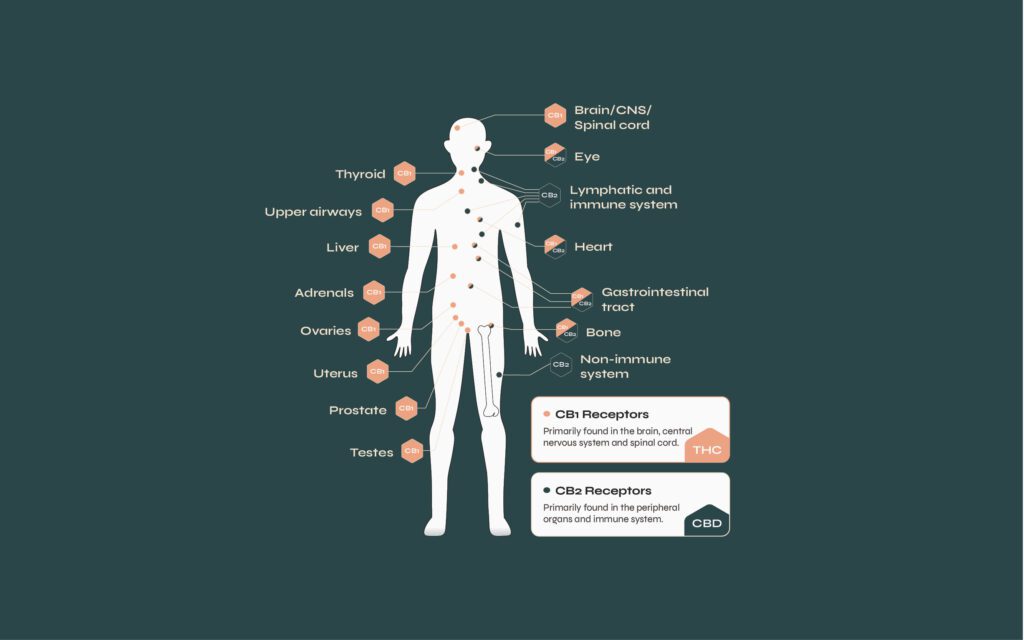
Endocannabinoid receptors receive and interact with endocannabinoid molecules are have, again, two key placements in the body:
CB1 receptors are primarily located throughout the Central Nervous System (CNS), and in particular the brain, also making these receptors part of the psychotropic effect of some medicinal components. These receptors, once activated by endocannabinoid molecules, help to enhance or moderate the release of neurotransmitters, influencing things like pain.
CB2 receptors are primarily found in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and throughout the immune system, playing a huge role in reducing immune responses, like chronic and acute inflammation.
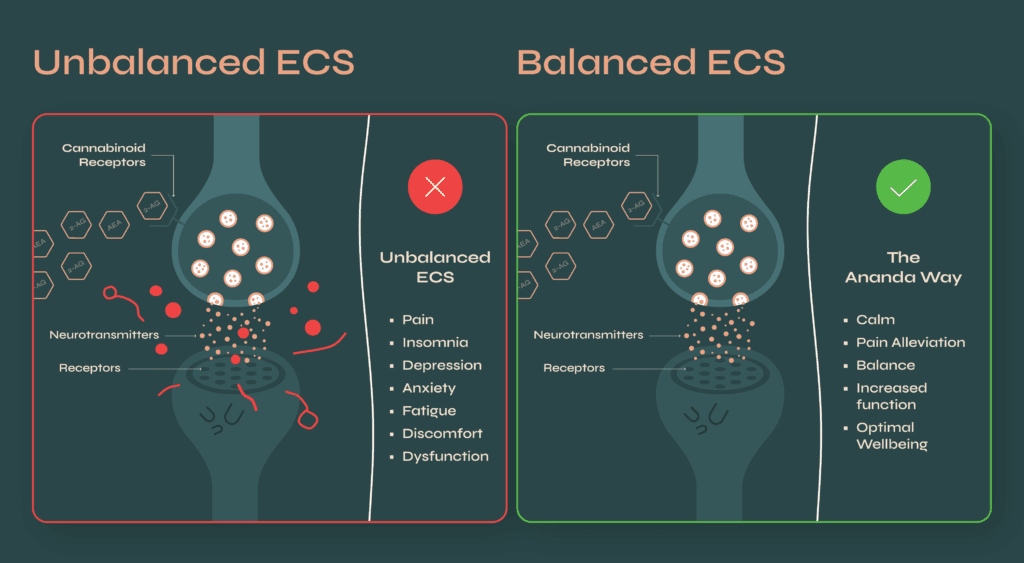
As a naturally existing biological system, the ECS regulates the release of endocannabinoids and the interaction with endocannabinoid receptors to help maintain homeostasis within your body.
The ECS is triggered by day-to-day activities like vigorous exercise, inflammation, pain, temperature changes and much, much more. Once activated, the endocannabinoid system sends out its endocannabinoids, or chemical messengers, to the different receptors sites as needed. Each endocannabinoid produced and released then binds to one of many receptors found all over the body (CB1+ CB2), effectively activating your body’s own ability to rebound, recover and heal.
When a receptor is engaged, whether it be a CB1 or CB2, things like pain, inflammation, anxiety, insomnia and seizures are regulated.
Dysfunction of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) can lead to unpredictable symptoms like, anxiety, depression, inflammation, insomnia, and uncontrollable mood swings.
Phytocannabinoids (phyto- meaning ‘from plants’), are naturally occurring molecules found in numerous plant species. Phytocannabinoids have a nearly identical chemical structure to the endocannabinoids naturally produced by the body and interact with receptor sites in nearly identical ways.
When ingested in precise, measured ways, phytocannabinoids can replicate our body’s natural endocannabinoids in order to regulate and influence the bodys’ neurological, endocrine, immune, and nervous system responses.
Ready to find out how your Endocannabinoid System may be influencing your symptoms, and can be used to help relieve those symptoms?
Find out more by Booking an appointment with a GP.
DISCLAIMER: The Ananda Clinics blog is here to provide education and information, without implying medical advice, or recommendation for the use of cannabis as medicine or adult use purposes.
Medical cannabis remains strictly regulated by the Australian TGA as it is not a registered therapeutic agent due to the lack of research and evidence in support of its efficacy or potential side effects.
If you think medical cannabis may be right for you, book an appointment with one of our doctors to find out more.
